TurboNuclease
for nucleic acid digestion to reduce viscosity of protein sample / Benzonase equivalent
TurboNuclease™ is a recombinant form of Serratia marcescens extracellular endonuclease (encoded by the same gene of Bezonase) produced in E. coli using a proprietary process. This nonspecific endonuclease hydrolyzes both single- and double -stranded nucleic acids (DNA and RNA) to 5’-phosphorylated oligonucleotides of 1-4 bases in length. TurboNuclease™ is a highly purified homodimer of 27 kDa subunits that has exceptional high specific activity and is free of protease activity. TurboNuclease™ is ideal for digesting nucleic acids during virus preparation and for reducing cell lysate viscosity during protein purification.
Features
- Affordable ultra-pure Nuclease (Benzonase equivalent)
- Free of protease activity
Activity and Specificity
One unit of TurboNuclease converts 1 OD260 of salmon sperm DNA into acidsoluble nucleotides in 30 minutes at 37°C in a reaction buffer of 50 mM Tris-HCl, pH 8.0 and 1 mM MgCl2. This corresponds to complete digestion of 50 ug of salmon sperm DNA into oligonucleotides. TurboNuclease has a specific activity of >1.3x106 units/mg. This is equivalent to >3x106 Kunitz units/mg, over 100-fold specific activity of most highly purified bovine DNase I (~25,000 Kunitz units/mg).
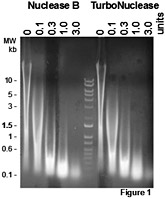
Figure 1
50 ug of salmon sperm DNA was incubated with the indicated units of TurboNuclease and another brand of nuclease at 37°C for 30 minutes in a buffer of 50 mM Tris-HCl, pH 8.0 and 1 mM MgCl2. DNA digestion was monitored by agarose gel. TurboNuclease shows no detectable protease activity.
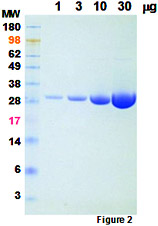
Formulation and Purity
Storage
Application
Downloads
Instruction
Ordering Information
| Product | Storage | Cat.No. | PKG Size | Price | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TurboNuclease (250 units/ul) | -20°C | NU0103P | 10,000 units | 94.00 | Buy |
| TurboNuclease (250 units/ul) | -20°C | NU0103S | 25,000 units | 174.00 | Buy |
| TurboNuclease (250 units/ul) | -20°C | NU0103M | 50,000 units | 291.00 | Buy |
| TurboNuclease (250 units/ul) | -20°C | NU0103L | 250,000 units | 1,096.00 | Buy |
